We will create a storage account and try to enable service endpoints in it. Such that the storage account can be accessed only inside the specified network. So we create a VNET and restrict access to components inside the VNET.
1. We create a storage account and create a container and upload an image to the blob container.
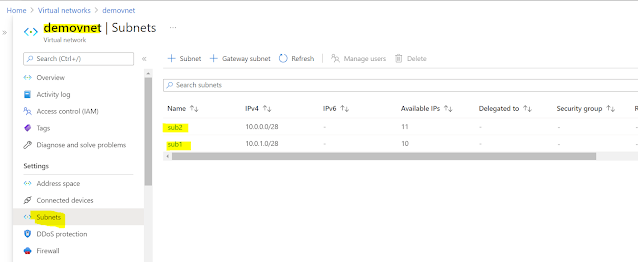
2. Next we create a VNET and add 2 subnets.
3. We then enable networking on the storage account by traffic only from the first subnet.
This will enable service endpoints in the subnet
Note that the second subnet doesnt have a service endpoint configured. So access is specific to a VNET and a subnet inside it (not to all subnets in it).
4. Then we try to view the uploaded blob in the browser (wont work).
6. Inside the VM if we try to access the same blob we find that we are able to view the image.
7. The same storage account cannot be accessed from the azure portal as well if the IP has not been added in the firewall configuration.









Comments
Post a Comment